AI training, validation, and testing data represent the three foundational phases of dataset usage in AI development. Under the EU AI Act, these phases must be governed by strict standards to ensure that AI systems are fair, accurate, and robust—especially for high-risk applications. The integrity and quality of each data phase are critical for achieving lawful and trustworthy AI performance throughout the lifecycle.
1. Background and Establishment
Data is the substrate of machine learning. Whether building a language model, a fraud detection tool, or an autonomous vehicle system, the training, validation, and testing datasets are the foundation upon which everything else stands.
The EU Artificial Intelligence Act identifies this foundational role and imposes strict legal obligations for how these datasets must be collected, governed, and used—particularly for high-risk AI systems that can affect individuals’ rights, freedoms, or safety.
2. Purpose and Role in the AI Lifecycle
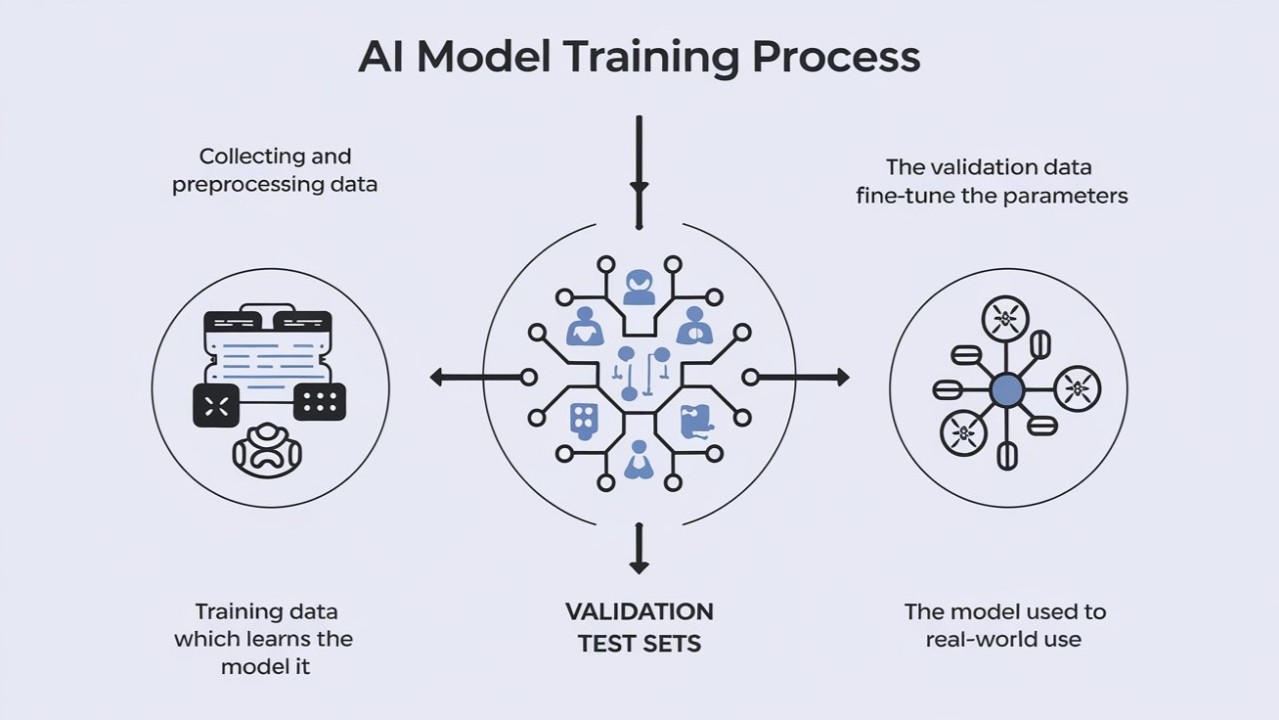
Each dataset phase serves a distinct role:
- Training data teaches the model underlying patterns through exposure to labeled examples.
- Validation data fine-tunes the model and helps prevent overfitting by guiding adjustments during training.
- Testing data evaluates the final model’s performance on unseen inputs, ensuring it generalizes well and is not biased.
Together, these stages form a complete evaluation pipeline—critical for ensuring AI systems behave reliably, fairly, and in compliance with EU law.
3. Legal Foundations in the EU AI Act
The EU AI Act mandates specific standards for dataset governance under:
Article 10 – Requires that training, validation, and testing datasets used in high-risk AI systems be:
- Relevant, representative, free of errors, and complete
- Appropriate in terms of statistical properties for the intended purpose
- Sourced and processed in a way that respects data protection law
Annex IV – Requires providers to document:
- Dataset composition and collection methods
- Dataset preprocessing and annotation
- Bias detection and correction strategies
These obligations are legally binding and essential for conformity assessments and CE marking.
4. The Role of the EU AI Safety Alliance
The EU AI Safety Alliance supports organizations with:
- Data phase-specific governance templates
- Dataset audit protocols for each phase (training, validation, testing)
- Bias detection tools and fairness scoring dashboards
- Guidance on alignment with GDPR, ISO/IEC 42001, and CEN-CENELEC AI standards
By leveraging Alliance resources, providers ensure that every dataset phase is legally compliant, technically sound, and ethically defensible.
5. Common Pitfalls in Dataset Development
Frequent issues include:
- Labeling errors or inconsistencies in training data
- Data leakage between training and testing sets, leading to inflated accuracy
- Unrepresentative validation data, which fails to reflect real-world deployment
- Bias due to imbalanced class distributions or skewed demographics
- Incomplete documentation of dataset lineage, making auditability difficult
Such issues can lead to regulatory non-compliance, model underperformance, or discriminatory behavior.
6. Best Practices for Dataset Governance Across All Phases
To ensure high-quality, compliant data:
Training phase:
- Use diverse, representative datasets
- Track sources, licensing, and consent
- Preprocess data to minimize noise and bias
Validation phase:
- Maintain strict separation from training data
- Use this phase to tune hyperparameters and monitor fairness
- Simulate deployment scenarios for realism
Testing phase:
- Ensure total independence from training/validation
- Perform disaggregated performance analysis (e.g. across age, gender, ethnicity)
- Document accuracy, error rates, and fairness metrics
All phases must be documented in Annex IV technical files and made available for review by Notified Bodies or market surveillance authorities.
7. How to Ensure Compliance with Dataset Requirements
To meet your obligations under the EU AI Act:
- Conduct a data audit to classify datasets by phase (train/validate/test)
- Document dataset sources, quality metrics, and intended use
- Evaluate datasets for representativeness and bias
- Align dataset management with Article 10 and GDPR
- Use EU AI Safety Alliance tools to support evaluation and traceability
- Regularly retrain and retest models when datasets evolve or environments change
- Be prepared to justify your data choices during audits or regulatory inquiries
Data governance is not a single step—it is an iterative, lifecycle-wide responsibility.

